ABC400(a-d)

A
输入x
输出400%x
B
直接累加,累加过程中
res+=pow(n,i),如果res>1e9,则输出inf,否则最后输出答案。
C
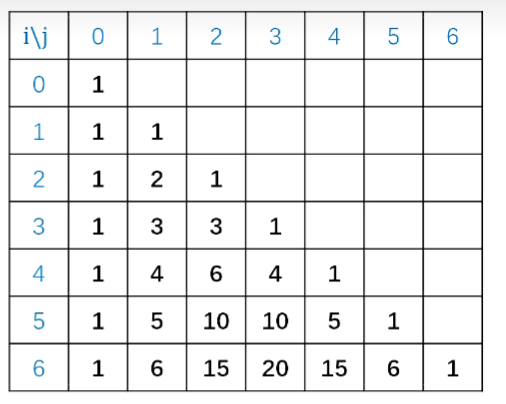
在做题过程中打表发现了 当a=1和a=2的时候能够表示1-n的所有好数。
下面是打表关键部分
1 |
|

暴力思路@kkkey11
由于2的幂次在之后会有重复的情况,那么就直接枚举不是2的倍数的b。
1 |
|
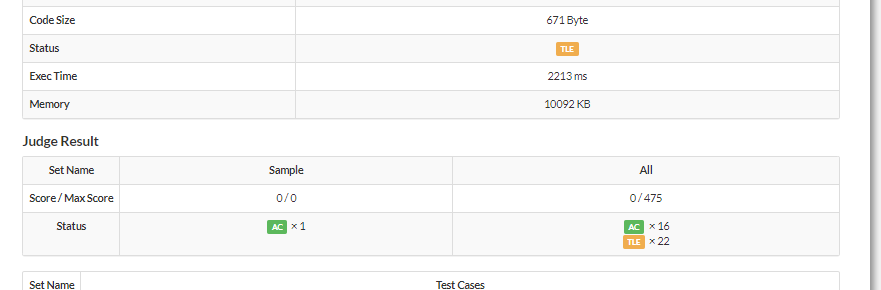
赛时打表没有用
sqrtl,被卡精度了。
1 |
|
D
赛后看了蔡的代码。
发现是用了双端队列
一开始自己做了一下,发现还是和01bfs有点区别,因为可能在在bfs过程中出现更新的距离比在队列前面的距离要小的情况。
需要注意,只有产生更小距离才入队
1 |
|
用优先队列会慢一点。
1 |
|
- Title: ABC400(a-d)
- Author: wlwhonest
- Created at : 2025-04-06 00:11:28
- Updated at : 2025-04-06 22:00:28
- Link: https://blog.wlwhonest.top/2025/04/06/ABC400-a-d/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
推荐阅读
推荐阅读
Comments